Scheduled for launch in November 2031, EnVision is ESA’s next medium-class mission to Venus. Its goal is to trace the planet’s evolution “from core to cloud tops” and to understand why Earth’s twin followed such a radically different path. The payload combines a powerful S-band radar (VenSAR), a subsurface sounder, radio-science experiments, and the three-channel VenSpec Suite to probe Venus’s surface composition, interior activity and atmosphere in unprecedented detail.
Within this suite, the Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía – CSIC is responsible for the dedicated power-supply units that serve the CCU itself and two of the three optical channels: VenSpec-H (high-resolution infrared) and VenSpec-U (ultraviolet). This contribution ensures a common, high-reliability power architecture across the instrument while easing overall mass and complexity.
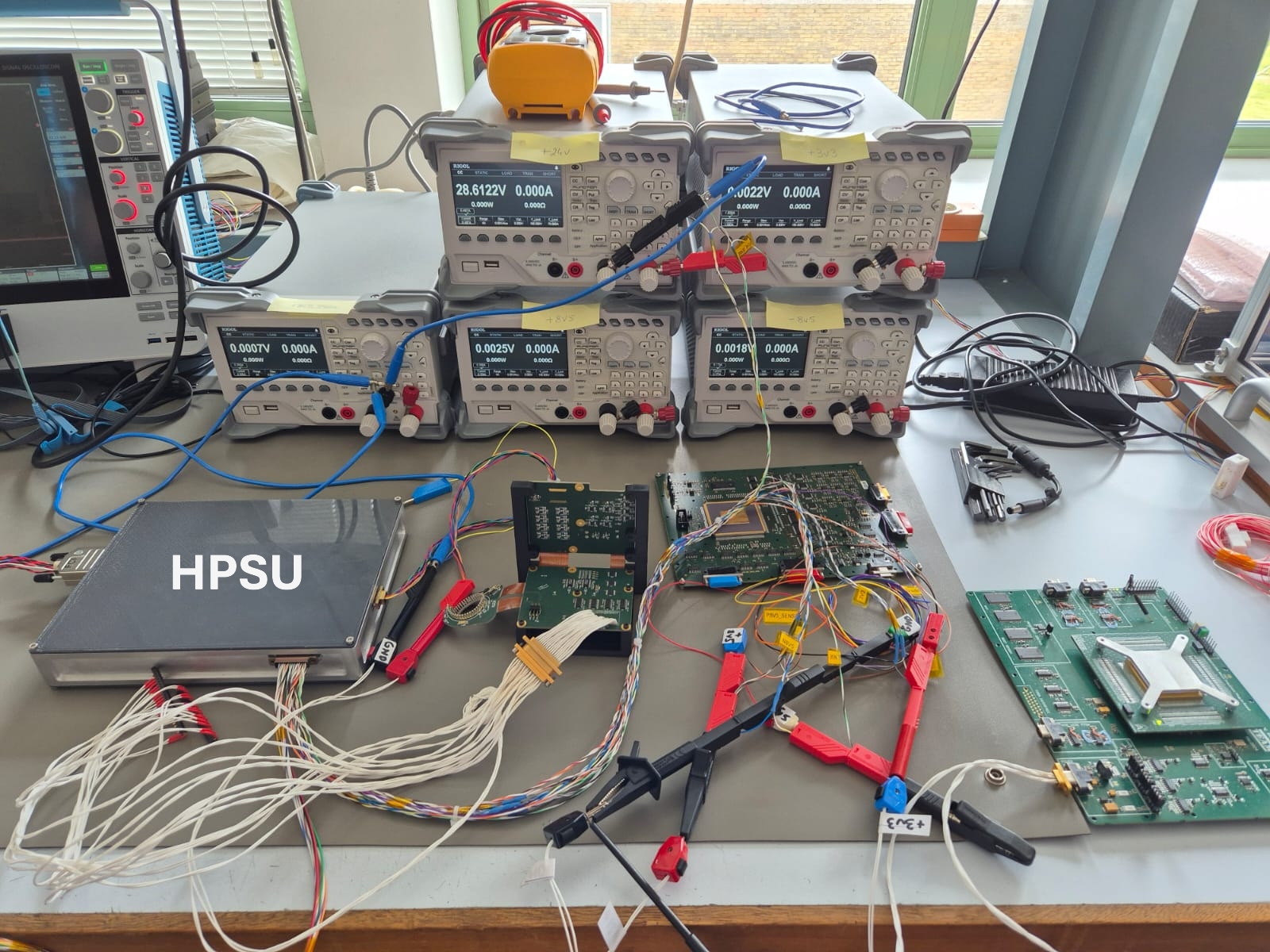
During May and June, engineers of SCITECHSS completed and successfully integrated the Pre-Engineering-Model (Pre-EM) power supply units for two key elements of ESA’s EnVision Venus orbiter:
- Central Control Unit (CCU) – the instrument’s “brain”, is the interface between the spacecraft and the instrument, responsible for commanding and data handling, and for distributing power among the VenSpec channels.
- VenSpec-H – the high-resolution infrared spectrometer within the VenSpec Suite.
Both power supplies were developed under the responsibility of the Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía – CSIC, and their smooth integration with the corresponding modules marks an important milestone on the road to flight hardware. During the campaign, we rigorously validated the functional requirements of each unit:
- Voltage / current levels for every output rail
- Built-in over-voltage, over-current and thermal protections
- Accurate telemetry acquisition of output voltages, currents and temperature sensors
- Autonomous fault-detection and recovery logic verified at system level
With the Pre-EM phase successfully completed, work is already underway on the Engineering Models (EM) in collaboration with Sener Aeroespacial.